| Suchergebnisse für "Borealer Nadelwald" im Seydlitz Weltatlas - Baden-Württemberg (978-3-507-01161-8) |
|---|
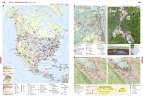 |
Nord- und Mittelamerika - Wirtschaft
Seite: 198-199
Stichwörter: Alberta, Artenschutz, BIP, BNE, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, Cluster, Dienstleistungszentrum, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Fernerkundung, First Nation, Flussverschmutzung, Gewässerbelastung, GNP, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kalifornien, Kanada, Kommunikation, Landschaftswandel, Luftfahrtindustrie, Mittelamerika, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Rodung, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, Standortfaktoren, Tagebau, Teer, Urbevölkerung, USA, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
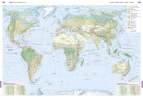 |
Erde - Bodenbedeckung
Seite: 242-243
Stichwörter: Alberta, Artenschutz, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, Cluster, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Fernerkundung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Flussverschmutzung, Gewässerbelastung, GNP, Golfstrom, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kalifornien, Kanada, Kommunikation, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Luftfahrtindustrie, Mittelamerika, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Rodung, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, Standortfaktoren, Tagebau, Teer, Trockenwald, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
 |
Erde - Geozonen
Seite: 244-245
Stichwörter: Alberta, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Fernerkundung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Flussverschmutzung, Geozone, Gewässerbelastung, GNP, Golfstrom, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Luftfahrtindustrie, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Rodung, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, Standortfaktoren, Subtropen, Tagebau, Teer, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
| Suchergebnisse für "Borealer Nadelwald" im Seydlitz Weltatlas - Bayern (978-3-507-01162-5) |
|---|
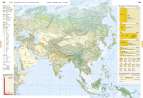 |
Asien - Vegetationszonen • Landwirtschaft
Seite: 138-139
Stichwörter: Alberta, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Asien, Banane, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Fernerkundung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Fleischwirtschaft, Flussverschmutzung, Geozone, Getreide, Gewässerbelastung, GNP, Golfstrom, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kaffee, Kakao, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Landwirtschaft, Luftfahrtindustrie, Mais, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Reis, Rodung, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, Standortfaktoren, Subtropen, Tagebau, Teer, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetation, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Zuckerrohr, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
 |
Russland - Transformationsprozesse
Seite: 146-147
Stichwörter: Agglomeration, Alberta, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Asien, Automobilindustrie, Ballungsgebiet, Ballungsraum, Banane, Bevölkerungsveränderung, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, City, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Fernerkundung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Fleischwirtschaft, Flussverschmutzung, Fragmentierte Stadt, Fragmentierung, Gated Community, Gentrifizierung, Geozone, geschlossene Wohnkomplexe, Getreide, Gewässerbelastung, Global Cities, Global City, GNP, Golfstrom, Großwohnsiedlung, Hauptgeschäftszentrum, Hauptstadt, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kaffee, Kakao, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landbevölkerung, Landflucht, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Landwirtschaft, Luftfahrtindustrie, ländliche Siedlung, Mais, Metropole, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Moskau, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Reis, Rodung, Russland, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Sibirien, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, sozialistische Planstadt, Stadtkern, Stadtteil, Stadtviertel, Standortfaktoren, Subtropen, Tagebau, Taiga, Teer, Trabantenstadt, Transformationsprozesse, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetation, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Weltstadt, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Zentrale Orte, Zuckerrohr, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
 |
Nord- und Mittelamerika - Landwirtschaft
Seite: 196-197
Stichwörter: Agglomeration, Agrarindustrie, Agroindustrie, Alberta, Anbaugrenze, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Asien, Automobilindustrie, Ballungsgebiet, Ballungsraum, Banane, Bevölkerungsveränderung, Bewässerung, Bewässerungssysteme, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, City, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Export, Feedlot, Fernerkundung, Fernwasserleitung, Fernwasserversorgung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Fleischwirtschaft, Flussverschmutzung, Fragmentierte Stadt, Fragmentierung, Gated Community, Gemüseanbau, Gentrifizierung, Geozone, geschlossene Wohnkomplexe, Getreide, Gewässerbelastung, Global Cities, Global City, GNP, Golfstrom, Großwohnsiedlung, Hauptgeschäftszentrum, Hauptstadt, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, industrial farming, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kaffee, Kakao, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landbevölkerung, Landflucht, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Landwirtschaft, Luftfahrtindustrie, ländliche Siedlung, Mais, Metropole, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Moskau, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Obstanbau, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Reis, Rindermast, Rodung, Russland, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Sibirien, Silicon Valley, Sonderkulturen, soziale Medien, sozialistische Planstadt, Stadtkern, Stadtteil, Stadtviertel, Standortfaktoren, Staudamm, Stausee, Steigungsregen, Subtropen, Tagebau, Taiga, Talsperre, Teer, Trabantenstadt, Transformationsprozesse, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetation, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Veredelungsbetrieb, Versorgung, Viehwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserferntransport, Wasserverschmutzung, Wasserversorgung, Wasserwirtschaft, Weinbau, Weltstadt, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Zentrale Orte, Zuckerrohr, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
 |
Nord- und Mittelamerika - Wirtschaft
Seite: 198-199
Stichwörter: Agglomeration, Agrarindustrie, Agroindustrie, Alberta, Anbaugrenze, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Asien, Automobilindustrie, Ballungsgebiet, Ballungsraum, Banane, Bevölkerungsveränderung, Bewässerung, Bewässerungssysteme, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, City, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Export, Feedlot, Fernerkundung, Fernwasserleitung, Fernwasserversorgung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Fleischwirtschaft, Flussverschmutzung, Fragmentierte Stadt, Fragmentierung, Gated Community, Gemüseanbau, Gentrifizierung, Geozone, geschlossene Wohnkomplexe, Getreide, Gewässerbelastung, Global Cities, Global City, GNP, Golfstrom, Großwohnsiedlung, Hauptgeschäftszentrum, Hauptstadt, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, industrial farming, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kaffee, Kakao, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landbevölkerung, Landflucht, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Landwirtschaft, Luftfahrtindustrie, ländliche Siedlung, Mais, Metropole, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Moskau, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Obstanbau, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Reis, Rindermast, Rodung, Russland, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Sibirien, Silicon Valley, Sonderkulturen, soziale Medien, sozialistische Planstadt, Stadtkern, Stadtteil, Stadtviertel, Standortfaktoren, Staudamm, Stausee, Steigungsregen, Subtropen, Tagebau, Taiga, Talsperre, Teer, Trabantenstadt, Transformationsprozesse, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetation, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Veredelungsbetrieb, Versorgung, Viehwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserferntransport, Wasserverschmutzung, Wasserversorgung, Wasserwirtschaft, Weinbau, Weltstadt, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Zentrale Orte, Zuckerrohr, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
 |
Erde - Bodenbedeckung
Seite: 242-243
Stichwörter: Agglomeration, Agrarindustrie, Agroindustrie, Alberta, Anbaugrenze, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Asien, Automobilindustrie, Ballungsgebiet, Ballungsraum, Banane, Bevölkerungsveränderung, Bewässerung, Bewässerungssysteme, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, City, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Export, Feedlot, Fernerkundung, Fernwasserleitung, Fernwasserversorgung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Fleischwirtschaft, Flussverschmutzung, Fragmentierte Stadt, Fragmentierung, Gated Community, Gemüseanbau, Gentrifizierung, Geozone, geschlossene Wohnkomplexe, Getreide, Gewässerbelastung, Global Cities, Global City, GNP, Golfstrom, Großwohnsiedlung, Hauptgeschäftszentrum, Hauptstadt, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, industrial farming, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kaffee, Kakao, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landbevölkerung, Landflucht, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Landwirtschaft, Luftfahrtindustrie, ländliche Siedlung, Mais, Metropole, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Moskau, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Obstanbau, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Reis, Rindermast, Rodung, Russland, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Sibirien, Silicon Valley, Sonderkulturen, soziale Medien, sozialistische Planstadt, Stadtkern, Stadtteil, Stadtviertel, Standortfaktoren, Staudamm, Stausee, Steigungsregen, Subtropen, Tagebau, Taiga, Talsperre, Teer, Trabantenstadt, Transformationsprozesse, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetation, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Veredelungsbetrieb, Versorgung, Viehwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserferntransport, Wasserverschmutzung, Wasserversorgung, Wasserwirtschaft, Weinbau, Weltstadt, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Zentrale Orte, Zuckerrohr, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
 |
Erde - Geozonen
Seite: 244-245
Stichwörter: Agglomeration, Agrarindustrie, Agroindustrie, Alberta, Anbaugrenze, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Asien, Automobilindustrie, Ballungsgebiet, Ballungsraum, Banane, Bevölkerungsveränderung, Bewässerung, Bewässerungssysteme, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, City, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Export, Feedlot, Fernerkundung, Fernwasserleitung, Fernwasserversorgung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Fleischwirtschaft, Flussverschmutzung, Fragmentierte Stadt, Fragmentierung, Gated Community, Gemüseanbau, Gentrifizierung, Geozone, geschlossene Wohnkomplexe, Getreide, Gewässerbelastung, Global Cities, Global City, GNP, Golfstrom, Großwohnsiedlung, Hauptgeschäftszentrum, Hauptstadt, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, industrial farming, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kaffee, Kakao, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landbevölkerung, Landflucht, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Landwirtschaft, Luftfahrtindustrie, ländliche Siedlung, Mais, Metropole, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Moskau, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Obstanbau, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Reis, Rindermast, Rodung, Russland, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Sibirien, Silicon Valley, Sonderkulturen, soziale Medien, sozialistische Planstadt, Stadtkern, Stadtteil, Stadtviertel, Standortfaktoren, Staudamm, Stausee, Steigungsregen, Subtropen, Tagebau, Taiga, Talsperre, Teer, Trabantenstadt, Transformationsprozesse, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetation, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Veredelungsbetrieb, Versorgung, Viehwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserferntransport, Wasserverschmutzung, Wasserversorgung, Wasserwirtschaft, Weinbau, Weltstadt, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Zentrale Orte, Zuckerrohr, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
| Suchergebnisse für "Borealer Nadelwald" im Seydlitz Weltatlas - Nordrhein-Westfalen (978-3-507-01163-2) |
|---|
 |
Asien - Vegetationszonen • Landwirtschaft
Seite: 138-139
Stichwörter: Agglomeration, Agrarindustrie, Agroindustrie, Alberta, Anbaugrenze, Artenschutz, Artenvielfalt, Asien, Automobilindustrie, Ballungsgebiet, Ballungsraum, Banane, Bevölkerungsveränderung, Bewässerung, Bewässerungssysteme, Biodiversität, BIP, BNE, Bodenbedeckung, Bodentypen, Bodenzone, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, City, Cluster, Dauerfrostboden, Dienstleistungszentrum, Dornstrauchsavanne, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erde, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Export, Feedlot, Fernerkundung, Fernwasserleitung, Fernwasserversorgung, Feuchtsavanne, First Nation, Fleischwirtschaft, Flussverschmutzung, Fragmentierte Stadt, Fragmentierung, Gated Community, Gemüseanbau, Gentrifizierung, Geozone, geschlossene Wohnkomplexe, Getreide, Gewässerbelastung, Global Cities, Global City, GNP, Golfstrom, Großwohnsiedlung, Hauptgeschäftszentrum, Hauptstadt, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, industrial farming, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kaffee, Kakao, Kalifornien, Kanada, Klimadiagramm, Klimazone, Kommunikation, Landbevölkerung, Landflucht, Landschaftsgürtel, Landschaftswandel, Landwirtschaft, Luftfahrtindustrie, ländliche Siedlung, Mais, Metropole, Mittelamerika, Mittelbreiten, Moskau, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Obstanbau, Permafrost, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Regenzeit, Reis, Rindermast, Rodung, Russland, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Savanne, Sibirien, Silicon Valley, Sonderkulturen, soziale Medien, sozialistische Planstadt, Stadtkern, Stadtteil, Stadtviertel, Standortfaktoren, Staudamm, Stausee, Steigungsregen, Subtropen, Tagebau, Taiga, Talsperre, Teer, Trabantenstadt, Transformationsprozesse, Trockenklima, Trockenwald, Trockenzeit, Tropen, Tropischer Regenwald, Tropische Zone, Tundra, Tundrenvegetation, Urbevölkerung, USA, Vegetation, Vegetationszone, Verbundwirtschaft, Veredelungsbetrieb, Versorgung, Viehwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserferntransport, Wasserverschmutzung, Wasserversorgung, Wasserwirtschaft, Weinbau, Weltstadt, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Wüste, Zentrale Orte, Zuckerrohr, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ökosysteme, Ökozone, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|