 |
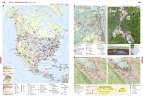
Nord- und Mittelamerika - Wirtschaft
Seite: 198-199
Stichwörter: Alberta, Artenschutz, BIP, BNE, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, Cluster, Dienstleistungszentrum, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Fernerkundung, First Nation, Flussverschmutzung, Gewässerbelastung, GNP, Hightech-Standorte, Human Footprint, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kalifornien, Kanada, Kommunikation, Landschaftswandel, Luftfahrtindustrie, Mittelamerika, Nadelwälder, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Rodung, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, Standortfaktoren, Tagebau, Teer, Urbevölkerung, USA, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
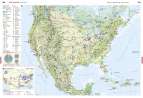 |
USA/Kanada - Wirtschaft
Seite: 200-201
Stichwörter: Alberta, Artenschutz, Atomenergie, Atomkraft, Atomkraftwerk, Außenhandel, Belt-System, Belts, Beltsystem, Bewässerung, BIP, BNE, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, Cluster, Dienstleistungszentrum, Eisenerzbergbau, Eisenverhüttung, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erdgas, Erdöl, Exploration, Export, Fernerkundung, First Nation, Flussverschmutzung, Gewässerbelastung, GNP, Hightech-Standorte, Holzwirtschaft, Human Footprint, Import, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industrieraum, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kalifornien, Kanada, Kernenergie, Kernkraft, Kernkraftwerk, Kommunikation, Landschaftswandel, Luftfahrtindustrie, Manufacturing Belt, Mexico, Mittelamerika, Nadelwälder, Nahrungsmittelindustrie, Naturlandschaft, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Rodung, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, Stahlerzeugung, Standortfaktoren, Strukturwandel, Sunbelt, Tagebau, Teer, Urbevölkerung, USA, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|
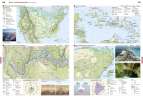 |
Nord- und Mittelamerika - Tourismus
Seite: 206-207
Stichwörter: Alberta, Arizona, Artenschutz, Atomenergie, Atomkraft, Atomkraftwerk, Außenhandel, Badetourismus, Belt-System, Belts, Beltsystem, Bewässerung, Biosphärenreservat, BIP, BNE, Borealer Nadelwald, Bruttoinlandsprodukt, Bruttonationaleinkommen, Cenote, Cluster, Dienstleistungszentrum, Eisenerzbergbau, Eisenverhüttung, Elektroauto, Energie, Energierohstoffe, Erdgas, Erdöl, Erosion, Exploration, Export, Fernerkundung, Ferntourismus, First Nation, Flussverschmutzung, Geologie, Gewässerbelastung, GNP, Grand Canyon, Hightech-Standorte, Hochkulturen, Holzwirtschaft, Hotel, Human Footprint, Höhle, Import, Indianer, Indigene, Industrieansiedlung, Industrieentwicklung, Industrieraum, Industriestandorte, Informationstechnik, Internet, IT, Kalifornien, Kanada, Karibik, Karst, Karstformen, Karstgestein, Kernenergie, Kernkraft, Kernkraftwerk, Kommunikation, Kreuzfahrten, Kreuzfahrttourismus, Kulturtourismus, Lagune, Landschaftswandel, Luftfahrtindustrie, Mangoven, Mangrovenwald, Manufacturing Belt, Massentourismus, Maya, Mexico, Mittelamerika, Nadelwald, Nadelwälder, Nahrungsmittelindustrie, Nationalpark, Naturlandschaft, Naturschutz, Naturtourismus, Nordamerika, Nutzungskonflikt, Plattentektonik, Produktionsverflechtung, Raumfahrtindustrie, Relief, Reservation, Rodung, San Francisco, Satellitenbild, Silicon Valley, soziale Medien, Stahlerzeugung, Standortfaktoren, Strukturwandel, Sunbelt, Tagebau, Teer, Tektonik, Tourismus, Touristen, Trockenwald, Urbevölkerung, USA, Verbundwirtschaft, Wasser, Wasserverschmutzung, Wirtschaft, Wirtschaftsstandorte, Wirtschaftszentren, Wirtschaftszentrum, Yucatán, Ökologischer Fußabdruck, Ölsande, ökologischer Fußabdruck
|